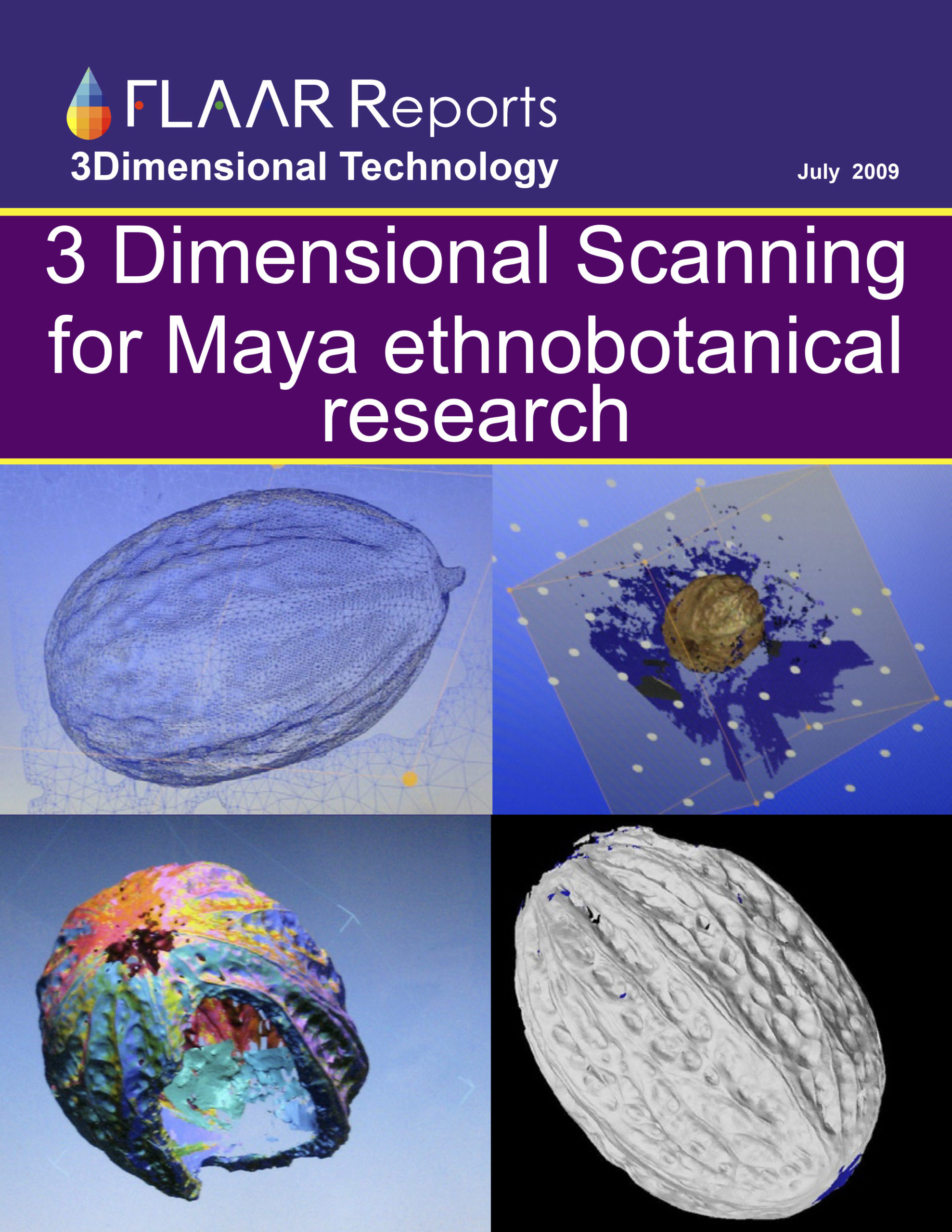
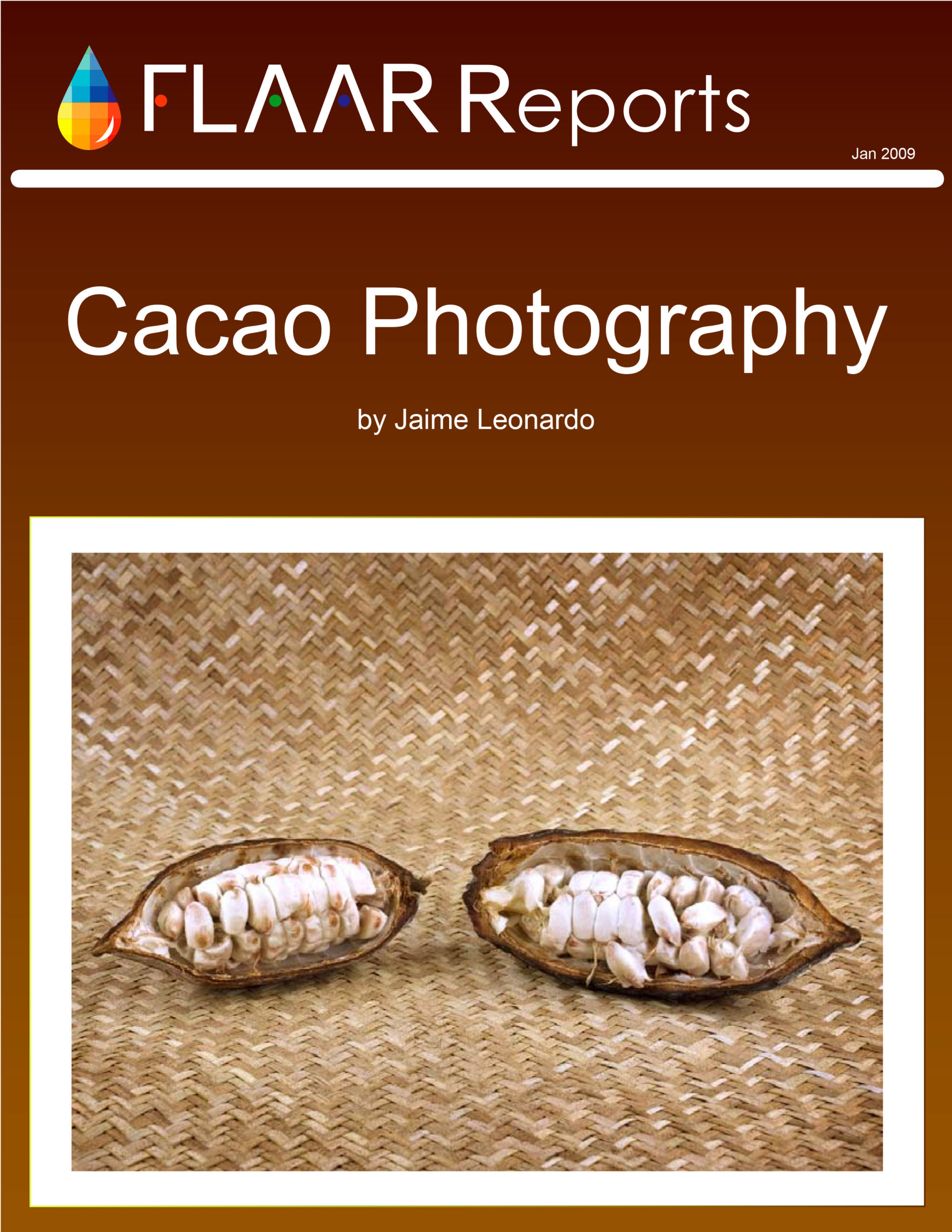
Bibliography on Agave americanaL., family Asparagaceae
Agave americana is the accepted name for the species of the genus Agave (family Asparagaceae) according to The Plant List (www.theplantlist.org). It is commonly called “Maguey”, “Maguey Blanco” or “Pita”.
Where can be found?
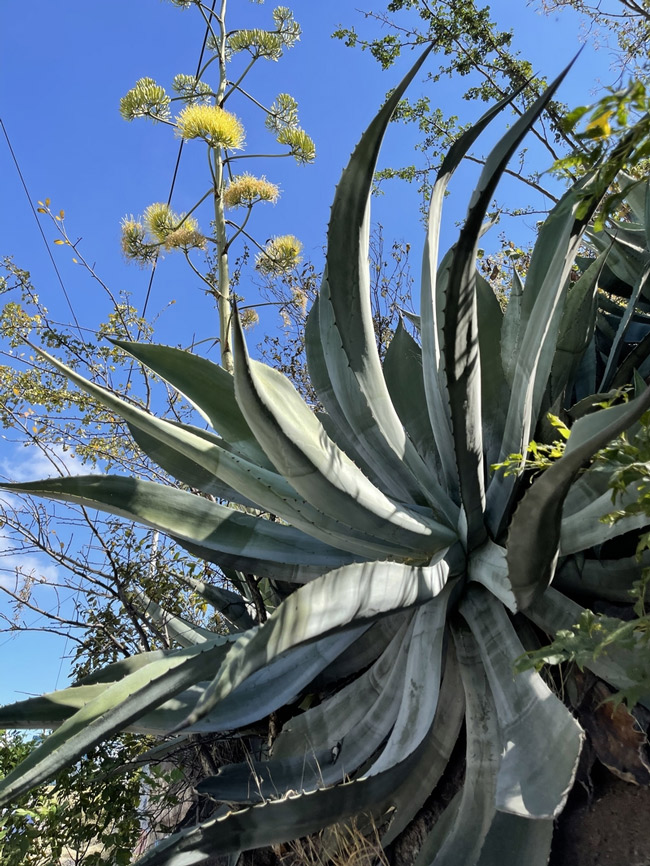
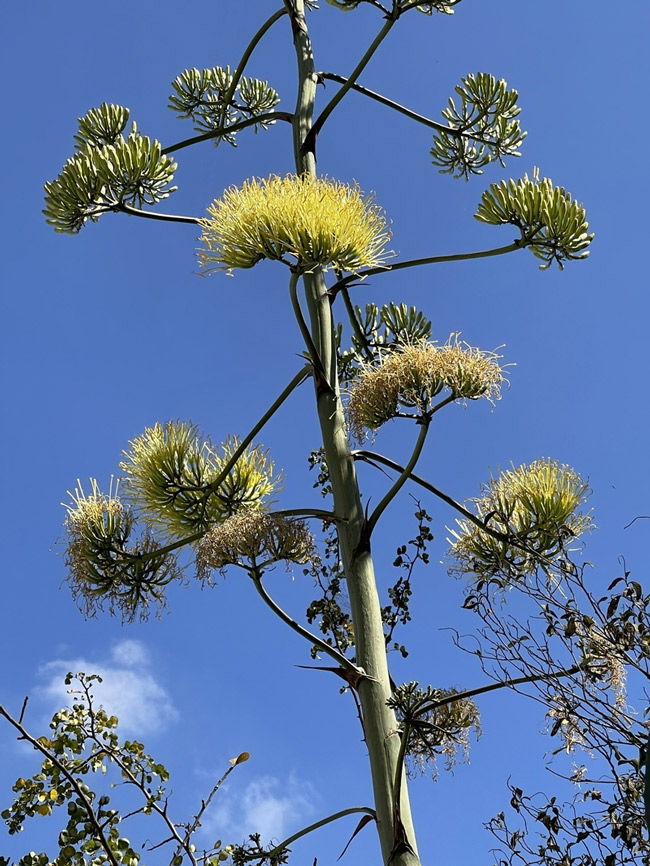
The plant is originally native to Mexico, Arizona and Texas but cultivated worldwide as an ornamental plant and naturalized in many regions of the world. It naturally grows in arid and semi-arid climates. The FLAAR Mesoamerica team documented an Agave americana blooming at Guastatoya, El Progreso, Km 52 of highway CA9.
Agave americana
Photographies by Nicholas Hellmuth (December, 2020)
Edible use
According to different authors, the plant can be eaten in many ways. The heart of the plant is very rich in saccharine matter and can be eaten when baked (Hendrick, 1972; Balls, 1975; Facciola, 1990). You can also ground the seed into a flour and use it as a thickener in soups or with cereal flours when making bread (Balls, 1975). The flower stalk can be roasted and used like asparagus (Balls, 1975; Facciola, 1990). The sap from the cut flowering stems is used as a syrup (Kunkel 1984) or fermented into pulque or mescal (Weiner, 1980)
Medical use
The sap of agaves has long been used in Central America as a binding agent for various powders used as poultices on wounds (Chevallier, 1996). In addition, the sap is antiseptic, diaphoretic, diuretic, emmenagogue and laxative (Lust, 1983).
The plant is used internally in the treatment of indigestion, flatulence, constipation, jaundice and dysentery (Brown, 1995). According to Peana et al (1997) Agave americana contains anti-inflammatory properties for gastrointestinal diseases treatment.
It is good a scalp disinfectant and tonic in cases of falling hair (Lust, 1983), for that reason you can find a lot of hair products based on A. americana extractions.
Other uses
Agave Americana leaves are harvested principally for fiber extraction. The production does not need agricultural chemicals, having a minimal environmental impact. During processing of Agave americana fibers, only organic waste is produced which can often be reused. The by-products after the processing of the agave takes the form of bio-degradable organic matter which can be used as “compost” or as an organic material to be returned to the land and as fuel for biogas production. In this way, they enhance soil fertility. Unlike synthetic fibers, Agave americana fiber is 100% biodegradable during its lifetime and Agave americana ropes and other products can be recycled as paper. The plants can be also used as an effective hedge to protect crops and land from predators and the extensive root system helps to reduce soil erosion in arid areas. It is also used as an ornamental plant and its flowering stems can be used for fencing.
PDF, Articles, Books on Agave americanaL., family Asparagaceae
- 1975
- Early Uses of Californian Plants. University of California Press.
- 1995
- Encyclopaedia of Herbs and their Uses. Dorling Kindersley, London
- 1981
- Las Plantas Cultivadas de México, Guatemala Y Colombia. IICA Biblioteca Venezuela. 216 pages.
- 1996
- The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants. Dorling Kindersley. London.
- 2017
- Los agaves y las prácticas mesoamericanas de aprovechamiento, manejo y
domesticación. Domesticación en el continente americano Vol. 2Edition:
Primera Chapter: 11. Universidad Nacional de México.
Available Online: www.researchgate.net/publication/316883938_Los_agaves_y_las_practicas_mesoamericanas_de_aprovechamiento_manejo_y_domesticacion_1
- 1990
- Cornucopia - A Source Book of Edible Plants. Kampong Publications
- 2007
- Los agaves de México. Ciencias 87.
Available Online: http://revistas.unam.mx/index.php/cns/article/viewFile/12113/11435
- 1972
- Sturtevant's Edible Plants of the World. Dover Publications.
- 2015
- Agave americana. Leaf fibers. Fibers 2015, 3, 64-75.
Available Online: www.mdpi.com/2079-6439/3/1/64
- 1984
- Plants for Human Consumption. Koeltz Scientific Books.
- 2013
- Elaboración, control de calidad y evaluación de la actividad antidiabética de la miel de Agave (Agave americana L.). Escuela superior politécnica de Chimborazo. Facultad de Ciencias. Escuela de Bioquímica y Farmacia.
Available Online: http://dspace.espoch.edu.ec/bitstream/123456789/3099/1/56T00408.pdf
- 1983
- The Herb Book. Bantam books.
- 2015
- Guía informativa de identificación taxonómica de las principales especies vegetales del campus central de la Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala. Dirección General de Investigación. 246 pages.
Information on Agave americana on page 144.
Available Online: https://digi.usac.edu.gt/edigi/pdf/guia.pdf
- n.d.
- El Agave (Agave americana L.) en las culturas prehispánicas: Una revisión bibliográfica. Chloris chilensis. Revista chilena de flora y vegetación, Año 10. No 1
Available Online: www.chlorischile.cl/pardoagave2/Agaveamericana2007.htm
- 2010
- Extracción de fibras de agave para elaborar papel y artesanías Acta Universitaria, vol. 20, núm. 3, pp. 77-83 Universidad de Guanajuato Guanajuato, México.
Available Online: www.redalyc.org/pdf/416/41618860011.pdf
- 1997
- Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Aqueous Extracts and Steroidal Sapogenins of Agave americana. Planta Medica, 63(03), 199–202.
Available Online: www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-2006-957652
- 1920
- Trees and Shrubs of Mexico. Contr. U.S. Nat. Herb. 23: 107- 142.
Available Online: www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/53162#page/7/mode/1up
- n.d.
- Identificación taxonómica de agaves (Agave spp.) utilizados para la elaboración del licor comiteco en Chiapas, México.
Available Online: http://revista-agroproductividad.org/index.php/agroproductividad/article/view/408/291
Suggested webpages with photos and information on Agave americana
https://cibercactus.com/agave-americana/
Information, characteristics and uses.
https://colombia.inaturalist.org/taxa/64103-Agave-americana
Information and photos.
https://esacademic.com/dic.nsf/eswiki/33583
Information.
First posted February 8, 2021
Written by Vivian Hurtado, manager of bibliography preparation, FLAAR Mesoamerica.